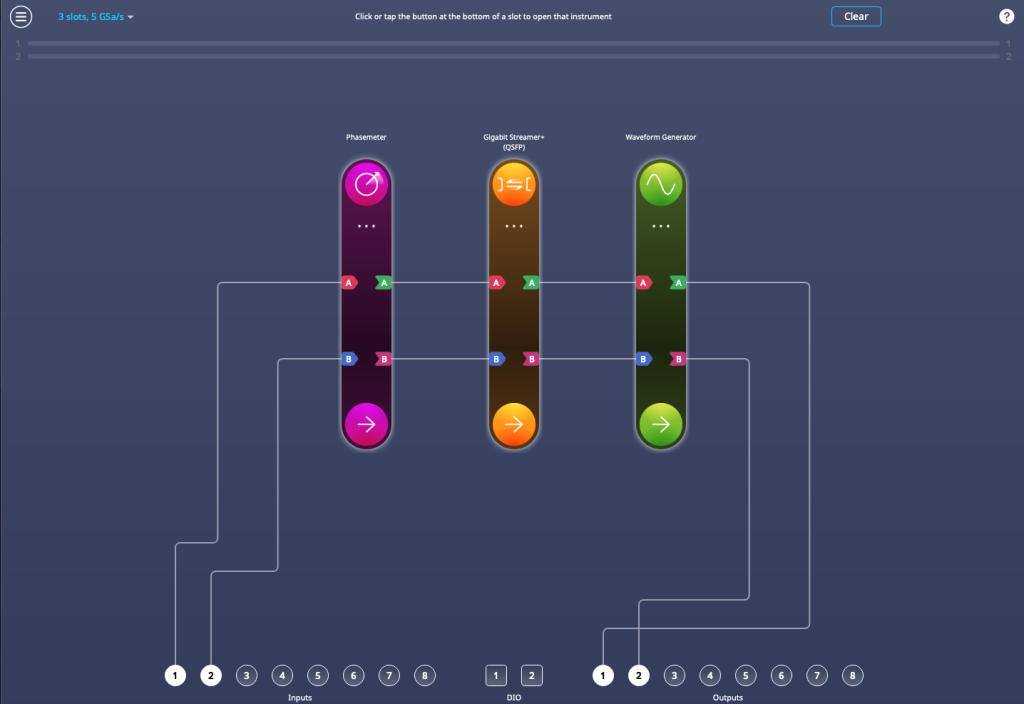
Gigabit Streamer now available on Moku:Delta
The new Gigabit Streamer allows Moku:Delta users to transmit and receive data at speeds of up to 312.5 MSa/s through SFP and up to 5 GSa/s through QSFP. Deploy it in Multi-Instrument Mode alongside instruments such as the Phasemeter to continuously stream measurement data to your host PC. With the option to interleave data on up to two ports, the Gigabit Streamer excels in high-speed data recording and playback applications such as quantum key distribution and communications.
Visit the new Gigabit Streamer Instrument page where you can find the specifications and data sheet. To download MokuOS 4.1 and view the instrument UI in demo mode, click here.
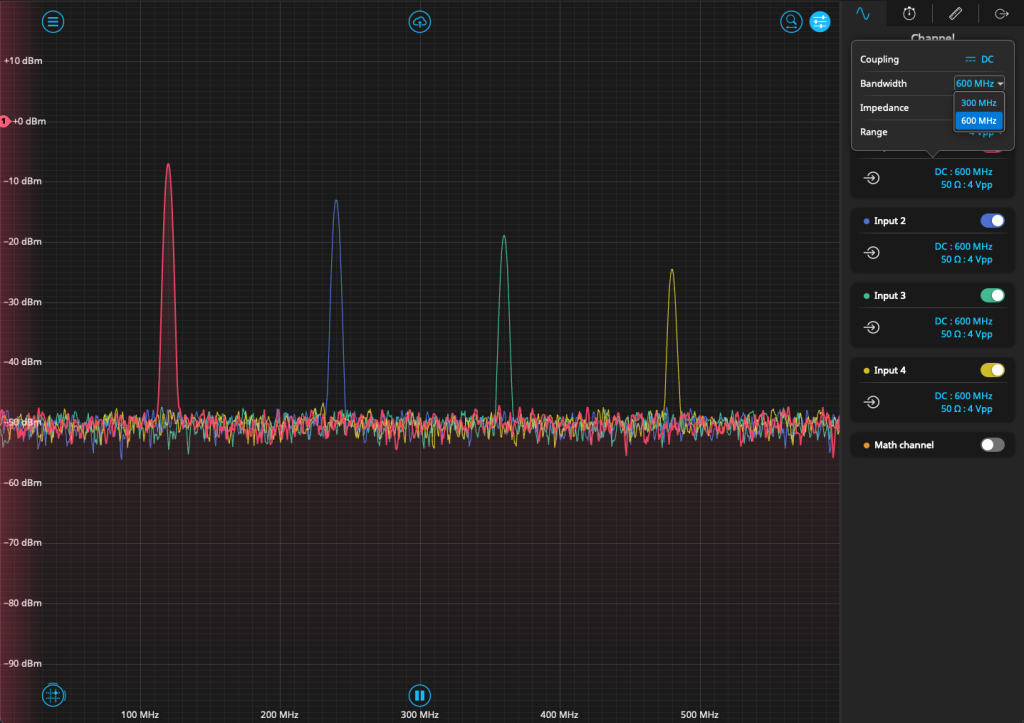
Configurable input bandwidth for Moku:Pro
In addition to the existing signal conditioning options on the Moku:Pro analog frontend, users now have the ability to switch the frequency of the input lowpass filter between 300 and 600 MHz. This allows users working at frequencies below 300 MHz to reduce the effects from higher frequency noise. This change also increases the range of Phasemeter and Spectrum Analyzer from their previous 300 MHz, with both instruments now measuring frequencies up to 600 MHz. You can find this option alongside other Input options (in single instrument mode), or by clicking on the input port number (in Multi-Instrument Mode).
Find out more about other Moku instruments on our Instruments page.
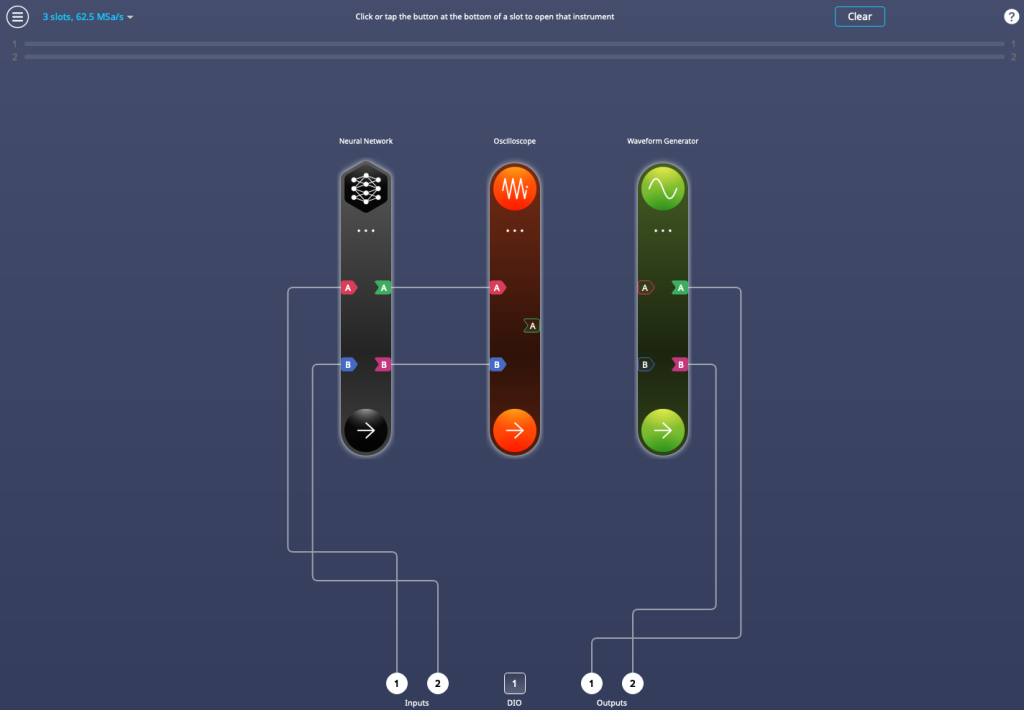
New instruments and features for Moku:Lab and Moku:Go
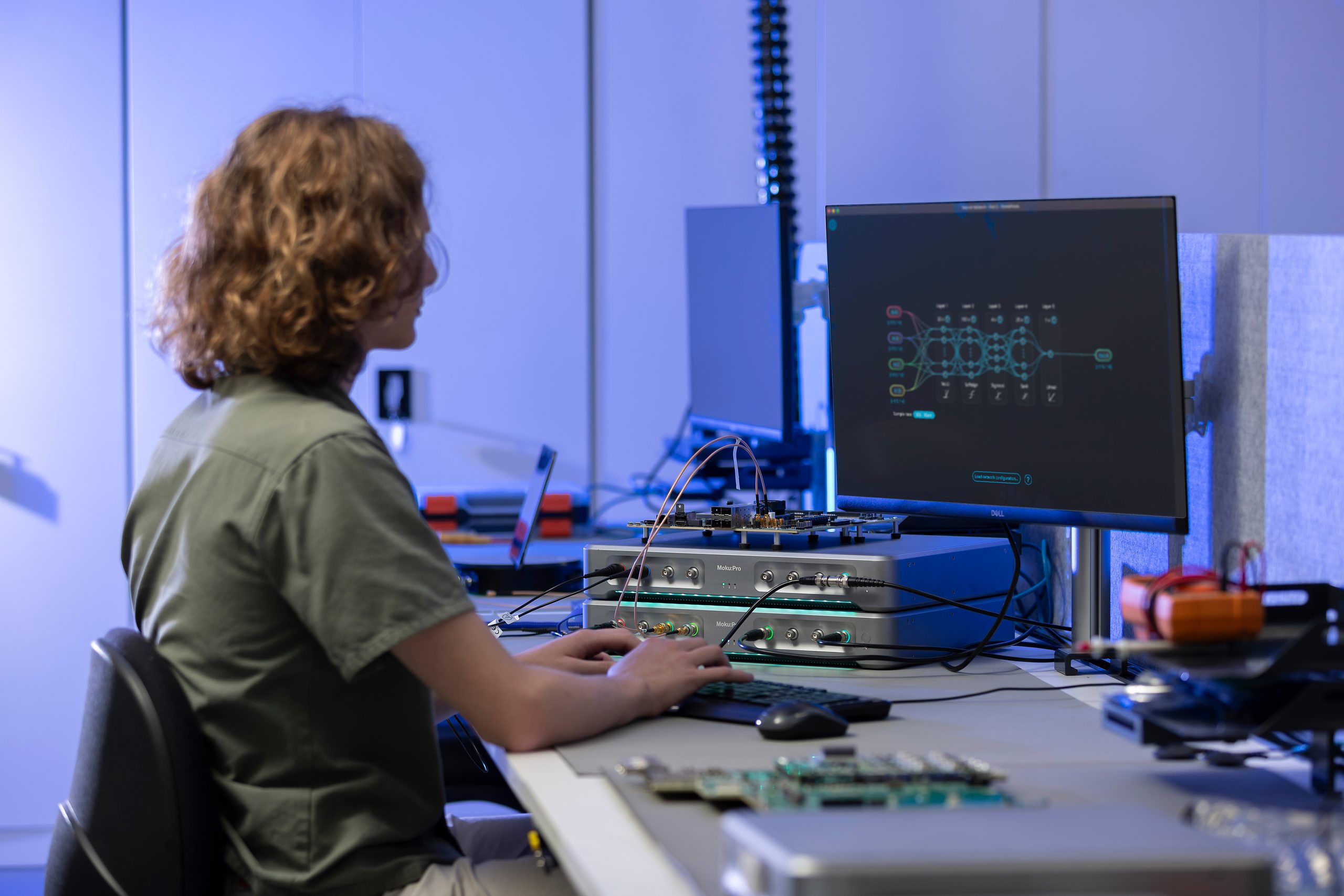
Last year, the Moku Neural Network was released for Moku:Pro. Now available on Moku:Go and Moku:Lab, users can deploy networks of up to five hidden layers of 80 neurons each, with the choice of five activation functions. To learn more about Neural Networks and their uses in test and measurement, read the blog post on the topic. To get started using the Neural Network on your Lab or Go, read the step-by-step tutorial on building, training, and deploying small-scale networks.
Moreover, Moku:Go and Moku:Lab now also feature an optional 3-slot Multi-Instrument Mode, selectable in the top left corner of the configuration screen. Users can select between 2-slot Multi-Instrument Mode for the maximum sampling rate, or 3-slot mode for more flexibility.
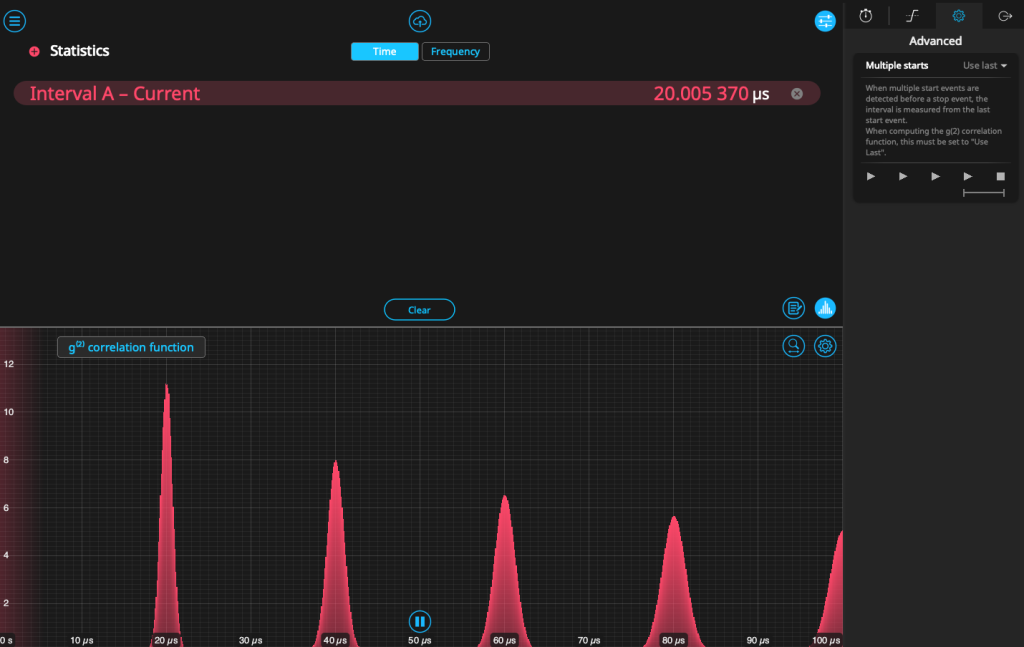
Measure correlation functions with Moku Time & Frequency Analyzer
One of the most requested features for the Moku Time & Frequency Analyzer is the ability to calculate the second-order correlation function g(2)(t) on the fly. This function provides information about the “quantumness” of a light source and is a figure of interest for a variety of quantum optics applications. When plotting event intervals, users can now switch from a histogram of the measured time intervals to the g(2)(t) correlation function, which updates in real time. This enables rapid measurement of correlations between events, and the information can be saved and transferred to your PC for further analysis.
For other types of time interval measurements, users can now specify how the Time & Frequency Analyzer handles multiple starts, using either the first or the last “start” event before a stop event is detected. Find this option under the “Advanced” tab on the configuration screen.
Learn more about single-photon counting from this webinar, or download the guide on Hanbury-Brown-Twiss measurements here.
Implement custom instruments
Moku Cloud Compile has renamed to distinguish it from the web-based compiler. Now called Moku Custom Instrument, it allows deployment of custom HDL code, which is written and compiled through Moku Cloud Compile*.
In addition, current users of Moku Custom Instrument will find that they can now read data back from their custom bitstreams through the status registers, and can also search for bitstreams through an in-app browser.
For configuration and pricing info, see here. To get started writing custom HDL code, read the application note on the topic.
*contact us for information about on-premise compile.






